Ensuring Compliance, Mitigating Risks, Driving Performance
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and addressing any financial, legal, strategic and security risks to an organization.
Business risks stem from many sources, including financial uncertainty, legal liabilities, technology use, strategic management errors, accidents and natural disasters. Risk management practices aim to anticipate these threats and their potential impact and establish plans to address them when they arise.

Comprehensive risk library
Quantitative risk assessment
Role-based remediation
Automated management workflows
Achieve Perseverance by Integrating Advanced Risk Intelligence
Integrating advanced risk intelligence enables organizations to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate potential threats. By leveraging real-time data analytics and predictive modeling, businesses can anticipate risks and implement effective strategies to address them. This proactive approach enhances decision-making, fosters a culture of resilience, and ensures sustained performance even in the face of challenges. Ultimately, integrating advanced risk intelligence empowers organizations to navigate uncertainties with confidence and achieve long-term success.
Risking uncertain outcomes without strategy makes you susceptible
This statement underscores the peril of navigating unknowns without a well-thought-out plan. In environments characterized by uncertainty, such as volatile markets or unpredictable global events, making decisions based solely on intuition or incomplete information can lead to significant vulnerabilities. Without a strategic approach, organizations may overlook potential risks or fail to capitalize on opportunities, ultimately compromising their resilience and long-term success
GRC Relates to Risk Management
Risk Identification and Assessment
GRC frameworks help organizations systematically identify and assess risks across various areas, including IT, finance, operations, and compliance.
Risk Mitigation
GRC provides tools and processes to mitigate identified risks, whether through controls, policies, or other measures.
Risk Monitoring
GRC frameworks facilitate the continuous monitoring of risks and the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies.
Compliance with Regulations
GRC ensures that organizations comply with relevant regulations, which often include risk management requirements.
Alignment with Business Objectives
GRC helps ensure that risk management efforts are aligned with the organization’s overall business objectives.

Types of risk Management
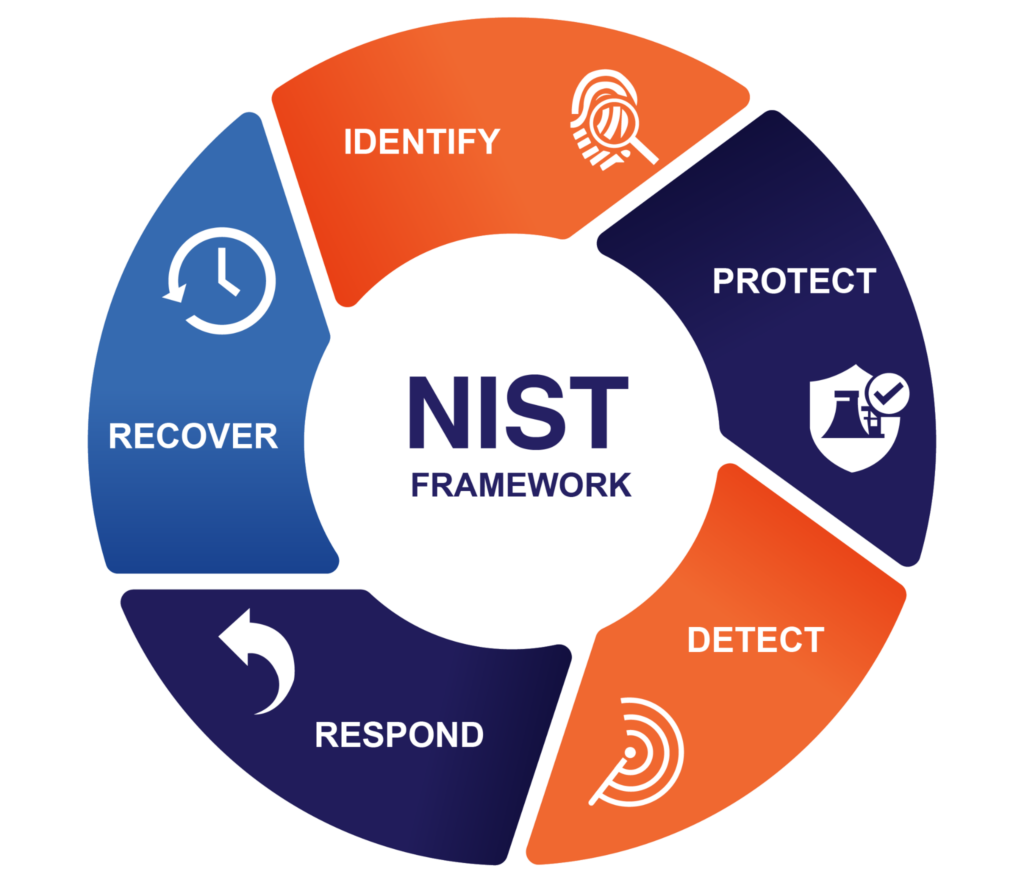
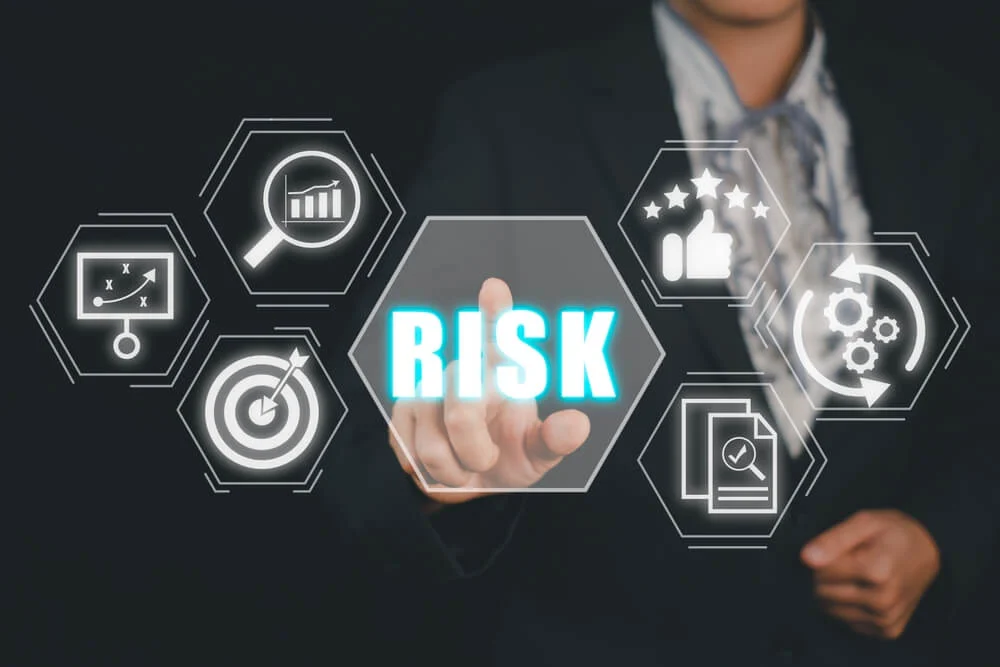
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a set of guidelines across five key functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—to help organizations establish a resilient cybersecurity posture. It is widely adopted for managing cybersecurity risks and is particularly useful for critical infrastructure sectors.
Prepare: Establish the context for risk management activities.
Categorize: Define information systems and determine impact levels.
Select: Choose appropriate security controls.
Implement: Apply selected controls.
Assess: Evaluate the effectiveness of controls.
Authorize: Make risk-based decisions to authorize system operation.
Monitor: Continuously oversee control effectiveness and system performance.